1. JSXTransformer
-
JSXTransformer 내부에서 사용되는 Esprima-FB 파서는 기존 Esprima 파서를 확장(JSX 명세) 구현한 버전이다.
-
현재 버전은 15001.1001.0-dev-harmony-fb 이며, 분석된 내용은 13001.1001.0-dev-harmony-fb 버전을 따른다.
-
-
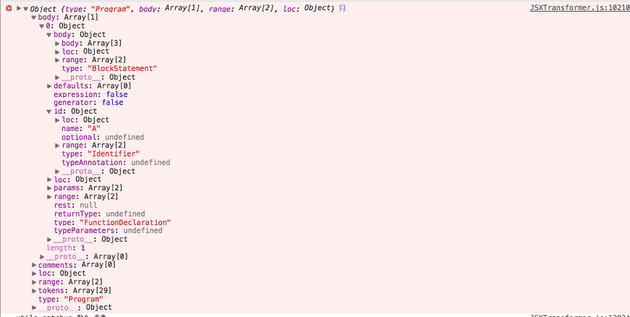
생성된 Parse 트리 구조는 모질라의 Parser AST 인터페이스 명세를 따르고 있다.(or 구현되어있다)
-
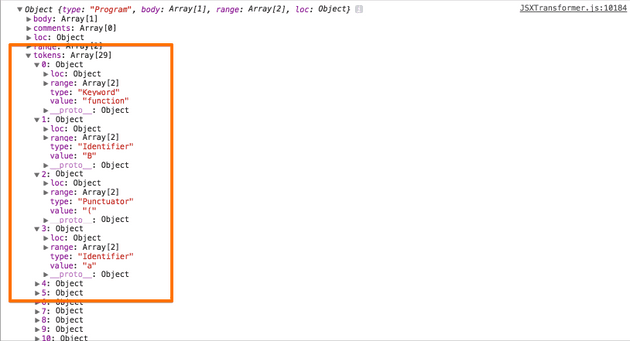
소스상의 parser 옵션 수정하여, (파서를 통해)수집된 토큰을 반환받을 수 있다.
function getAstForSource(source, options) { if (_astCache[source] && !options.disableAstCache) { return _astCache[source]; } var ast = esprima.parse(source, { // 아래와 같이 tokens 속성을 추가 한다. tokens: true, comment: true, loc: true, range: true, sourceType: options.sourceType }); if (!options.disableAstCache) { _astCache[source] = ast; } return ast; }
2. 소스 수집 및 Parse 트리 가 생성되는 과정
-
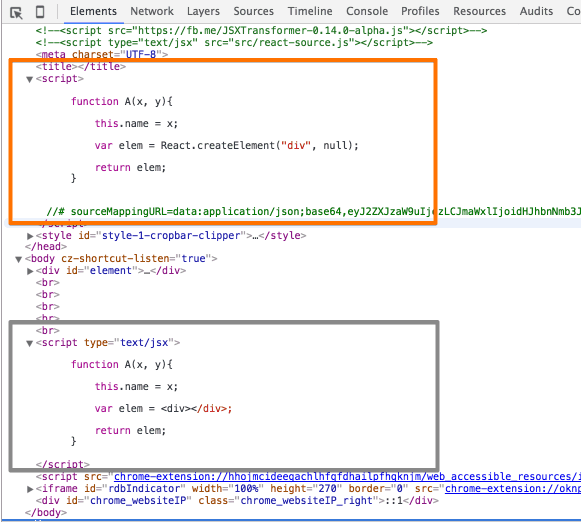
아래 소스는 Parser 에 의해 파싱될 원본 소스이다.
<script type="text/jsx"> function A(x, y){ this.name = x; var elem = <div></div>; return elem; } </script> -
소스 수집 과정
-
기본적으로 text/jsx 타입을 가진 Script Element 내부 소스(or 코드)는 브라우저에 의해 처리되지않는다.
<script type="text/jsx"> console.log('이 실행 코드는 브라우저에 의해 처리되지 않는다....'); </script> -
text/jsx 타입을 가진 모든 Script Element 를 수집한다.
function runScripts() { var scripts = document.getElementsByTagName('script'); // Array.prototype.slice cannot be used on NodeList on IE8 var jsxScripts = []; for (var i = 0; i < scripts.length; i++) { if (/^text\/jsx(;|$)/.test(scripts.item(i).type)) { jsxScripts.push(scripts.item(i)); } } ... // loadScripts 함수를 호출하여, script element 내부에 포함된 원본 소스를 가져온다. loadScripts(jsxScripts); } -
만약 inline code 로 작성된 경우에는 script.innerHTML 속성 값을 통해 소스를 가져오고, script.src 속성 값이 있는 경우에는 xhr 을 통해 가져온다.
// script.src 속성 값이 있는 경우 if (script.src) { result[i] = { async: async, error: false, executed: false, content: null, loaded: false, url: script.src, options: options }; // xhr 을 통해 해당 소스를 가져온다. load(script.src, function(content) { result[i].loaded = true; // content === source code result[i].content = content; check(); }, function() { result[i].error = true; check(); }); } else { // inline code 로 작성된 경우.. result[i] = { async: async, error: false, executed: false, content: script.innerHTML, loaded: true, url: null, options: options }; } -
수집된 원본 소스는 Parser 를 통해 파싱된 후, 새로운 Script Element 를 통해 로드 및 실행된다.
- 즉 생성된 Script Element 에 할당된 소스는 파싱된 소스를 가리킨다.
function run(code, url, options) { // script element 를 생성한다. var scriptEl = document.createElement('script'); // transformCode 함수를 통해 파서가 호출된다. scriptEl.text = transformCode(code, url, options); // 파서에 의해 파싱된 소스 console.log(scriptEl.text); // header element 의 자식 element 로 추가 시킨다. headEl.appendChild(scriptEl); } -
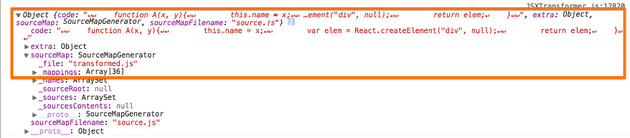
파싱된 소스 및 원본 소스
// 파서를 통해 파싱된 소스 function A(x, y){ this.name = x; var elem = React.createElement("div", null); return elem; }
-
-
Parse 트리 생성 과정
-
transformCode 함수가 호출된 후, 여러 단계(transformReact… , transform 등)를 거쳐, esprima.parse 함수를 통해, Parse 트리(AST)를 생성하는 함수인 getAstForSource 함수를 호출하게 된다.
function getAstForSource(source, options) { if (_astCache[source] && !options.disableAstCache) { return _astCache[source]; } // esprima 파서를 호출한다.(최종 파스 트리를 반환받는다) var ast = esprima.parse(source, { comment: true, loc: true, range: true, sourceType: options.sourceType }); if (!options.disableAstCache) { _astCache[source] = ast; } // 생성된 파스 트리를 반환한다. return ast; } -
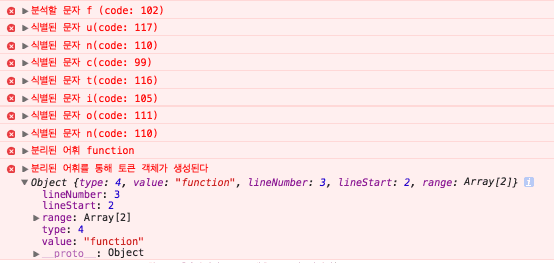
먼저 esprima.parse 함수가 호출되면, (여러 단계를 거친 후…) advance 함수를 통해 원본 소스에 포함된 각 문자(Char)의 의미를 분석 후, 분리된 토큰(어휘)을 객체화 시킨다.(내부적으로는 더 많은 단계를 거치게된다)
-
advance 함수 내부
function advance() { var ch; if (!state.inJSXChild) { skipComment(); } // 소스 분석이 종료되는 시점 // 현재 index(코드의 위치)가 length(포함된 소스의 전체 길이) 보다 크거나 같을경우 if (index >= length) { return { type: Token.EOF, lineNumber: lineNumber, lineStart: lineStart, range: [index, index] }; } // state.inJSXChild 가 true 인 경우(tag 열림('<') 상태가, 닫힘('>') 상태로 변경되었을 경우) // 즉 div element 가 닫힘('>') 문자로 인해 닫힌경우(단 열림('<') 문자 뒤에 '/' 문자가 오는 경우는 제외된다) if (state.inJSXChild) { return advanceJSXChild(); } // 원본 소스에 포함된 각 문자(Char)를 아스키 코드로 변환한다. ch = source.charCodeAt(index); /* 변환된 아스키 코드를 식별 후, 각 token 객체를 생성한다. */ // Very common: ( and ) and ; if (ch === 40 || ch === 41 || ch === 58) { return scanPunctuator(); } // String literal starts with single quote (#39) or double quote (#34). if (ch === 39 || ch === 34) { if (state.inJSXTag) { return scanJSXStringLiteral(); } return scanStringLiteral(); } if (state.inJSXTag && isJSXIdentifierStart(ch)) { return scanJSXIdentifier(); } if (ch === 96) { return scanTemplate(); } // 해당 문자의 의미를 분석 후, 토큰 객체를 생성한다. if (isIdentifierStart(ch)) { return scanIdentifier(); } // Dot (.) char #46 can also start a floating-point number, hence the need // to check the next character. if (ch === 46) { if (isDecimalDigit(source.charCodeAt(index + 1))) { return scanNumericLiteral(); } return scanPunctuator(); } if (isDecimalDigit(ch)) { return scanNumericLiteral(); } // Slash (/) char #47 can also start a regex. if (extra.tokenize && ch === 47) { return advanceSlash(); } return scanPunctuator(); }
-
-
예를들어, 위 isIdentifierStart 함수로 해당 아스키 코드(문자)의 의미를 분석 후, scanIdentifier 함수를 통해 토큰(어휘) 객체를 생성한다.
-
isIdentifierStart 함수 내부
function isIdentifierStart(ch) { // 해당 아스키 코드의 의미를 분석한다. return (ch === 36) || (ch === 95) || // $ (dollar) and _ (underscore) (ch >= 65 && ch <= 90) || // A..Z (ch >= 97 && ch <= 122) || // a..z (ch === 92) || // \ (backslash) ((ch >= 0x80) && Regex.NonAsciiIdentifierStart.test(String.fromCharCode(ch))); } -
scanIdentifier 함수 내부
function scanIdentifier() { var start, id, type; start = index; // Backslash (char #92) starts an escaped character. /* // 토큰 타입 Token = { BooleanLiteral: 1, EOF: 2, Identifier: 3, Keyword: 4, NullLiteral: 5, NumericLiteral: 6, Punctuator: 7, StringLiteral: 8, RegularExpression: 9, Template: 10, JSXIdentifier: 11, JSXText: 12 }; */ // 식별된 토큰이 id 변수로 할당된다. // 예: function(분리된 토큰 문자열) id = (source.charCodeAt(index) === 92) ? getEscapedIdentifier() : getIdentifier(); // There is no keyword or literal with only one character. // Thus, it must be an identifier. // 해당 토큰 타입을 설정한다.(식별자, 키워드, 일부 literal(null, boolean)) if (id.length === 1) { type = Token.Identifier; } else if (isKeyword(id)) { type = Token.Keyword; } else if (id === 'null') { type = Token.NullLiteral; } else if (id === 'true' || id === 'false') { type = Token.BooleanLiteral; } else { type = Token.Identifier; } // 생성된 토큰 객체를 반환한다. return { type: type, // 4(Keyword) value: id, // 'function' lineNumber: lineNumber, // 3 lineStart: lineStart, // 2 range: [start, index] // 6, 14 }; }
-
-
생성된 토큰(어휘) 객체를 통해 Parse(AST) 트리 구성을 위한 노드가 구성된다.
-
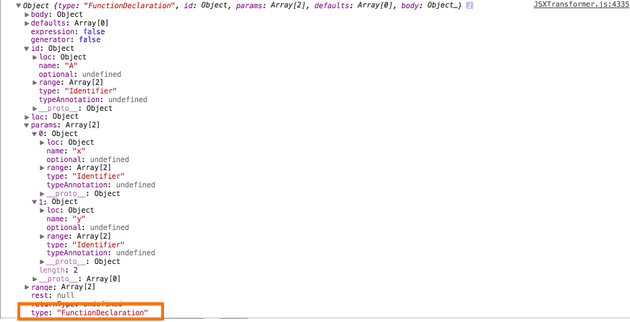
interface FunctionDeclaration <: Function, Declaration { // 노드 타입 type: "FunctionDeclaration"; // 해당 함수 선언식에 대한 식별자 정보 id: Identifier; } -
parseFunctionDeclaration 함수 내부
function parseFunctionDeclaration() { var id, body, token, tmp, firstRestricted, message, generator, isAsync, previousStrict, previousYieldAllowed, previousAwaitAllowed, marker = markerCreate(), typeParameters; isAsync = false; if (matchAsync()) { lex(); isAsync = true; } expectKeyword('function'); generator = false; if (match('*')) { lex(); generator = true; } token = lookahead; id = parseVariableIdentifier(); ... tmp = parseParams(firstRestricted); firstRestricted = tmp.firstRestricted; if (tmp.message) { message = tmp.message; } ... body = parseFunctionSourceElements(); ... // 함수 선언식에 대한 Parse 트리 노드를 생성한다. return markerApply( marker, delegate.createFunctionDeclaration( id, tmp.params, tmp.defaults, body, tmp.rest, generator, false, isAsync, tmp.returnType, typeParameters ) ); }
-
-
각 노드가 조합되어, 최종 Parse 트리가 생성된다.
-
utils.append, utils.catchup 함수(또 다른 함수 등)로 각 노드 객체 및 state 등을 전달하여, 최종 결과물인 파싱된 소스를 만들어 간다.(즉 source buffer 를 채워나간다)
-
utils.append 함수 내부
/** * Appends a string of text to the buffer * * @param {string} str * @param {object} state */ function append(str, state) { if (state.g.sourceMap && str) { state.g.sourceMap.addMapping({ generated: { line: state.g.bufferLine, column: state.g.bufferColumn }, original: { line: state.g.sourceLine, column: state.g.sourceColumn }, source: state.g.sourceMapFilename }); var transformedLines = str.split('\n'); if (transformedLines.length > 1) { state.g.bufferLine += transformedLines.length - 1; state.g.bufferColumn = 0; } state.g.bufferColumn += transformedLines[transformedLines.length - 1].length; } state.g.buffer += str; console.log(state.g.buffer); } -
utils.catchup 함수 내부
/** * Given a state fill the resulting buffer from the original source up to * the end * * @param {number} end * @param {object} state * @param {?function} contentTransformer Optional callback to transform newly * added content. */ function catchup(end, state, contentTransformer) { console.log('utils.catchup 함수 호출'); console.error(state); console.error('source position', state.g.position, end); if (end < state.g.position) { // cannot move backwards return; } var source = state.g.source.substring(state.g.position, end); var transformed = updateIndent(source, state); if (state.g.sourceMap && transformed) { // record where we are state.g.sourceMap.addMapping({ generated: { line: state.g.bufferLine, column: state.g.bufferColumn }, original: { line: state.g.sourceLine, column: state.g.sourceColumn }, source: state.g.sourceMapFilename }); // record line breaks in transformed source var sourceLines = source.split('\n'); var transformedLines = transformed.split('\n'); // Add line break mappings between last known mapping and the end of the // added piece. So for the code piece // (foo, bar); // > var x = 2; // > var b = 3; // var c = // only add lines marked with ">": 2, 3. for (var i = 1; i < sourceLines.length - 1; i++) { state.g.sourceMap.addMapping({ generated: { line: state.g.bufferLine, column: 0 }, original: { line: state.g.sourceLine, column: 0 }, source: state.g.sourceMapFilename }); state.g.sourceLine++; state.g.bufferLine++; } // offset for the last piece if (sourceLines.length > 1) { state.g.sourceLine++; state.g.bufferLine++; state.g.sourceColumn = 0; state.g.bufferColumn = 0; } state.g.sourceColumn += sourceLines[sourceLines.length - 1].length; state.g.bufferColumn += transformedLines[transformedLines.length - 1].length; } state.g.buffer += contentTransformer ? contentTransformer(transformed) : transformed; state.g.position = end; }
-
-
-
transform 함수를 통해, 최종 파싱된 소스가 포함된 객체를 반환하여, 소스 수집 과정에서 말한바와 같이 Script Element 를 통해 로드 및 실행된다.
function transform(visitors, source, options) { options = options || {}; var ast; try { // 파스 트리를 생성한다. ast = getAstForSource(source, options); } catch (e) { e.message = 'Parse Error: ' + e.message; throw e; } var state = utils.createState(source, ast, options); state.g.visitors = visitors; .... traverse(ast, [], state); utils.catchup(source.length, state); // state.g.buffer: 최종 파싱된 소스 var ret = {code: state.g.buffer, extra: state.g.extra}; .... // 파싱된 소스(ret.code)를 포함하는 객체를 반환한다. return ret; }